In this section, we provide guides and references to use the DRUID Connector
Step 1 –: Create New Service
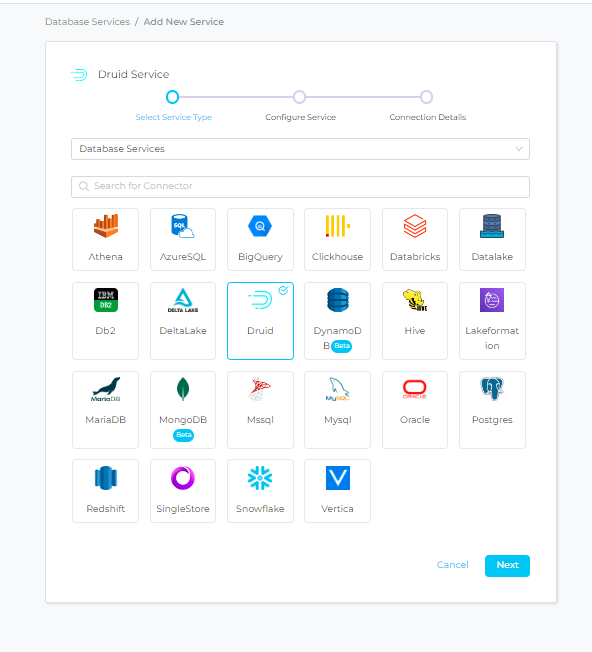
Step 2 –: Select DRUID Service Type
- Select DRUID as the Service type and click NEXT.
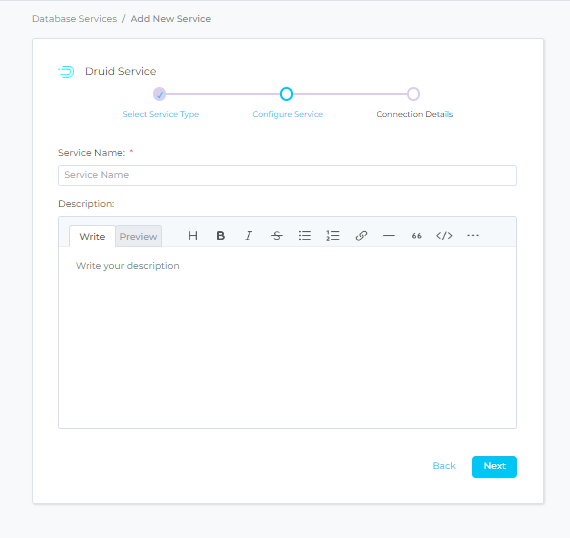
Step 3 –: Name and Describe Your Service
- Provide a name and description for your Service.
- Service Name: - Prakash uniquely identifies Services by their Service Name. Provide a name that distinguishes your deployment from other Services, including the other Druid Services that you might be ingesting metadata from.
Note that when the name is set, it cannot be change
Step 4 –: Configure The Service Connection
- In this step, we will configure the connection settings required for Athena
- Please follow the instructions below to properly configure the Service to read from your sources. You will also find helper documentation on the right-hand side panel in the UI.
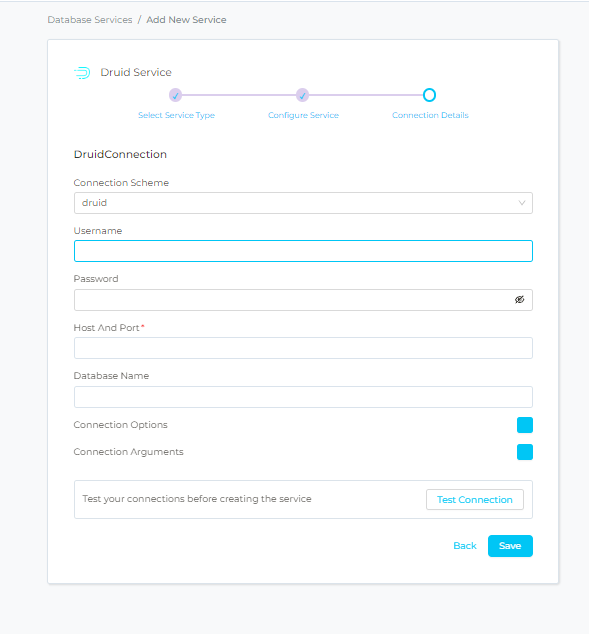
Connection Details : -
- Username: Specify the User to connect to druid. It should have enough privileges to read all the metadata.
- Password: Password to connect to druid
- Database: The database of the data source is an optional parameter, if you would like to restrict the metadata reading to a single database. If left blank, Prakash ingestion attempts to scan all the databases.
- Host and Port: Enter the fully qualified hostname and port number for your DRUID deployment in the Host and Port field.
Step 5 –: Check Test Connection
Once the credentials have been added, click on TEST CONNECTION To Check Credentials is valid or not.
If Test Connection Successful after that click on SAVE and then configure Metadata Ingestion.
Step 6 –: Configure Metadata Ingestion
In this step we will configure the metadata ingestion pipeline, Please follow the instructions below.
Step 7 –: Schedule the Ingestion and Deploy
- Scheduling can be set up at an hourly, daily, weekly, or manual cadence. The timezone is in UTC. Select a Start Date to schedule for ingestion. It is optional to add an End Date
- Review your configuration settings. If they match what you intended, click DEPLOY to create the service and schedule metadata ingestion
- If something doesn’t look right, click the BACK button to return to the appropriate step and change the settings as needed.
- After configuring the workflow, you can click on DEPLOY to create the pipeline.
Step 8 –: View the Ingestion Pipeline
Once the workflow has been successfully deployed, you can view the Ingestion Pipeline running from the Service Page
(IMG)
Step 9 –: Add Profiler Ingestion Pipeline
• Add Profiler Ingestion Pipeline to click on ADD INGESTION.
(IMG)
Step 10–: Configure Profiler Ingestion
- In this step we will configure the Profiler ingestion pipeline, please follow the instructions below.
Profiler Configuration:-
This workflow allows you to profile your table assets and gain insights into their structure (e.g. of metrics computed: max, min, mean, etc.)
Database Filter Pattern:-
- Database filter patterns to control whether to include database as part of metadata ingestion
- Include: Explicitly include databases by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Include field. Prakash will include all databases with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other databases will be excluded.
- For example, to include only those databases whose name starts with the word demo , add the regex pattern in the include field as ^demo.*
- Exclude: Explicitly exclude databases by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Exclude field. Prakash will exclude all databases with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other databases will be included
- For example, to exclude all databases with the name containing the word demo , add the regex pattern in the exclude field as .demo. .
Schema Filter Pattern:
- Schema filter patterns are used to control whether to include schemas as part of metadata ingestion.
- Include: Explicitly include schemas by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Include field. Prakash will include all schemas with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other schemas will be excluded.
- For example, to include only those schemas whose name starts with the word demo , add the regex pattern in the include field as ^demo.* .
- Exclude: Explicitly exclude schemas by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Exclude field. Prakash will exclude all schemas with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other schemas will be included.
- For example, to exclude all schemas with the name containing the word demo , add a regex pattern in the exclude field as .demo. .
Table Filter Pattern:
- Table filter patterns are used to control whether to include tables as part of metadata ingestion.
- Include: Explicitly include tables by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Include field. Prakash will include all tables with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other tables will be excluded.
- For example, to include only those tables whose name starts with the word demo , add the regex pattern in the include field as ^demo.* .
- Exclude: Explicitly exclude tables by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Exclude field. Prakash will exclude all tables with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other tables will be included
- For example, to exclude all tables with the name containing the word demo , add the regex pattern in the exclude field as .demo. .
Profile Sample:-
- Percentage of data or number of rows to use when sampling tables.
- By default, the profiler will run against the entire table.
Profile Sample Type:
- The sample type can be set to either:
o Percentage: this will use a percentage to sample the table (e.g. if table has 100 rows, and we set sample percentage tp 50%, the profiler will use 50 random rows to compute the metrics)
o Row Count: this will use a number of rows to sample the table (e.g. if table has 100 rows, and we set row count to 10, the profiler will use 10 random rows to compute the metrics)
Thread Count:
- Number of threads that will be used when computing the profiler metrics. A high number can have a negative performance effect.
- We recommend using the default value unless you have a good understanding of multi-threading and your database is capable of handling multiple concurrent connections.
Timeout (Seconds):
- This will set the duration a profiling job against a table should wait before interrupting its execution and moving on to profiling the next table.
- It is important to note that the profiler will wait for the hanging query to terminate before killing the execution. If there is a risk for your profiling job to hang, it is important to also set a query/connection timeout on your database engine. The default value for the profiler timeout is 12 hours.
Ingest Sample Data:
- Set the Ingest Sample Data toggle to control whether to ingest sample data as part of profiler ingestion. If this is enabled, 100 rows will be ingested by default.
Enable Debug Logs :
- Set the Enable Debug Log toggle to set the logging level of the process to debug. You can check these logs in the Ingestion tab of the service and dig deeper into any errors you might find.
Auto Tag PII :
- Set the Auto Tag PII toggle to control whether to automatically tag columns that might contain sensitive information as part of profiler ingestion
- If Ingest Sample Data is enabled, Prakash will leverage machine learning to infer which column may contain PII sensitive data. If disabled, Prakash will infer this information from the column name.
Then , Click on NEXT to configure Profiler Ingestion Pipeline
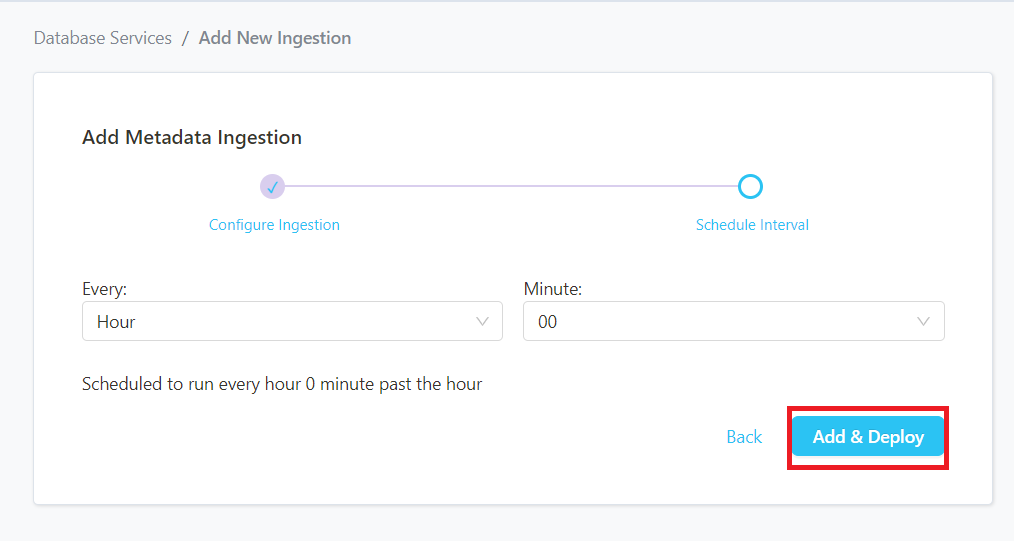
Step 11–: Schedule the Profiler Ingestion and Deploy
- Scheduling can be set up at an hourly, daily, weekly, or manual cadence. The timezone is in UTC. Select a Start Date to schedule for ingestion. It is optional to add an End Date
- Review your configuration settings. If they match what you intended, click ADD & DEPLOY to create the service and schedule Profiler ingestion
- If something doesn’t look right, click the BACK button to return to the appropriate step and change the settings as needed.
- After configuring the workflow, you can click on ADD & DEPLOY to create the pipeline
(Img)
Step 12 –: View the Profiler Ingestion Pipeline:
Once the workflow has been successfully deployed, you can view the Profiler Ingestion Pipeline running from the Service Page.
(IMG)